Understanding lung cancer: causes, early symptoms, lifestyle changes and modern treatments
Introduction to Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a significant health concern worldwide, impacting millions of individuals each year. As one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for both prevention and early intervention. This article delves into the complexities of lung cancer, providing insights that can aid in awareness and potentially improve outcomes for those affected.
Causes and Risk Factors
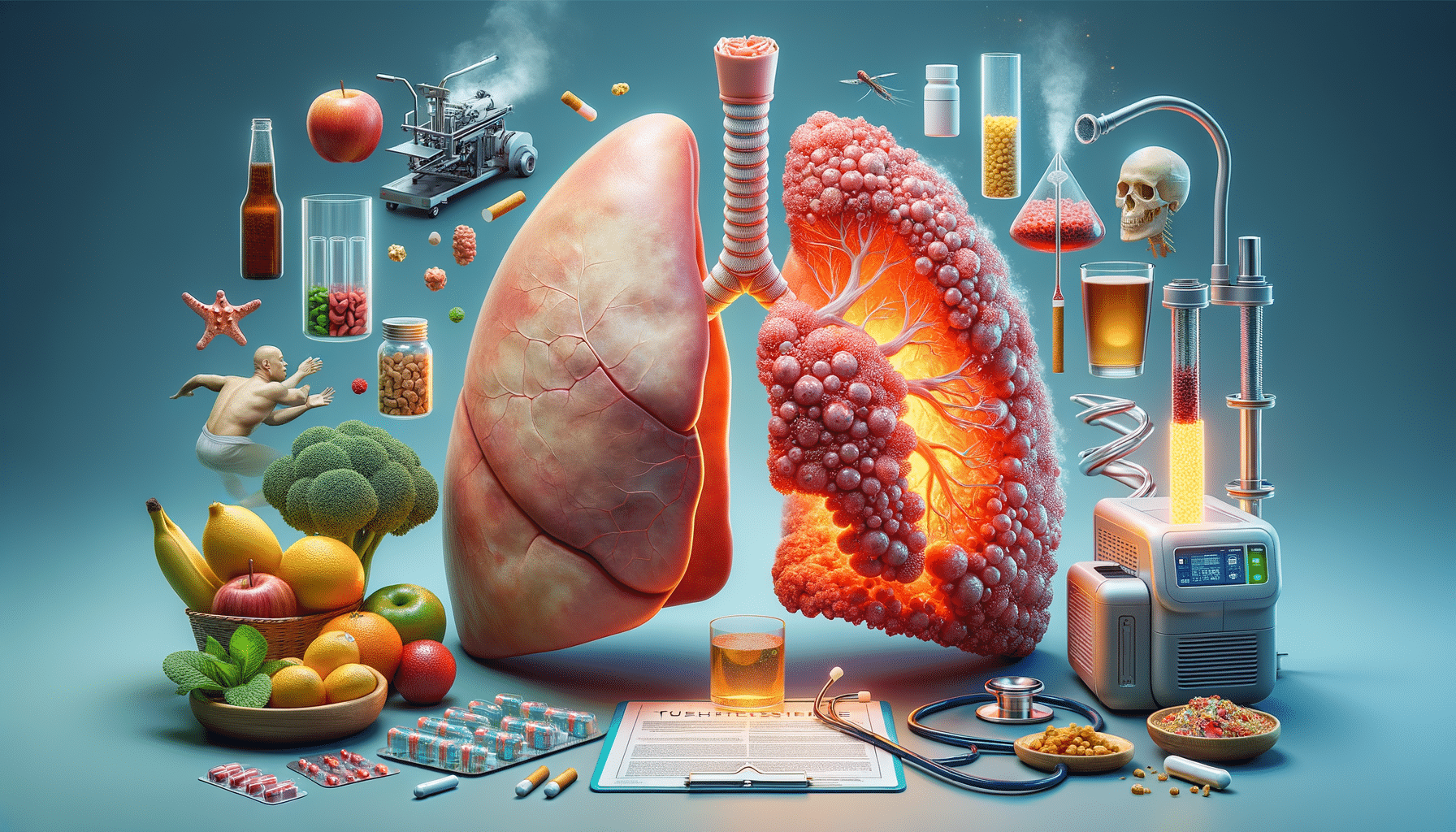
Lung cancer arises from mutations in the cells of the lungs, leading to uncontrolled growth and tumor formation. Several factors contribute to these mutations, with smoking being the most significant. Tobacco smoke contains numerous carcinogens that damage lung tissue over time, significantly increasing the risk of cancer. However, it’s important to note that non-smokers can also develop lung cancer due to other risk factors:
- Exposure to radon gas, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, can accumulate in homes and buildings.
- Asbestos exposure, often found in construction materials, is another risk factor.
- Air pollution, including fine particulate matter, has been linked to lung cancer.
- Genetic predisposition plays a role, as individuals with a family history of lung cancer may be at higher risk.
Understanding these risk factors is essential for taking preventive measures and reducing the incidence of lung cancer.
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis
Early detection of lung cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes, yet many cases are diagnosed at advanced stages due to subtle initial symptoms. Common early symptoms include a persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and unexplained weight loss. However, these symptoms are often mistaken for less severe conditions, delaying diagnosis.
Screening programs, such as low-dose CT scans, are recommended for high-risk individuals, particularly long-term smokers and those with a family history of lung cancer. These screenings can detect tumors at an earlier, more treatable stage. Diagnostic procedures like biopsies and imaging tests further confirm the presence and type of lung cancer, guiding treatment plans.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention and Management
While some risk factors for lung cancer, like genetic predisposition, cannot be controlled, lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce risk and aid in management. Quitting smoking is the most impactful change, as it reduces the risk of lung cancer and improves overall lung health. Support systems and cessation programs can assist individuals in overcoming nicotine addiction.
In addition to quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, regular physical activity, and avoiding exposure to known carcinogens are beneficial. For those diagnosed with lung cancer, these lifestyle changes can complement medical treatments, enhancing quality of life and potentially improving outcomes.
Modern Treatments and Innovations
The landscape of lung cancer treatment has evolved significantly, offering more hope for patients than ever before. Traditional treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, which remain vital in combating lung cancer. However, recent advancements have introduced targeted therapies and immunotherapy, which provide more personalized and effective treatment options.
Targeted therapies focus on specific genetic mutations within cancer cells, inhibiting their growth while sparing healthy cells. Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells, offering a promising alternative for patients with certain types of lung cancer.
These innovations, combined with ongoing research and clinical trials, continue to improve survival rates and quality of life for lung cancer patients. Staying informed about these developments empowers patients and caregivers to make informed decisions about treatment options.